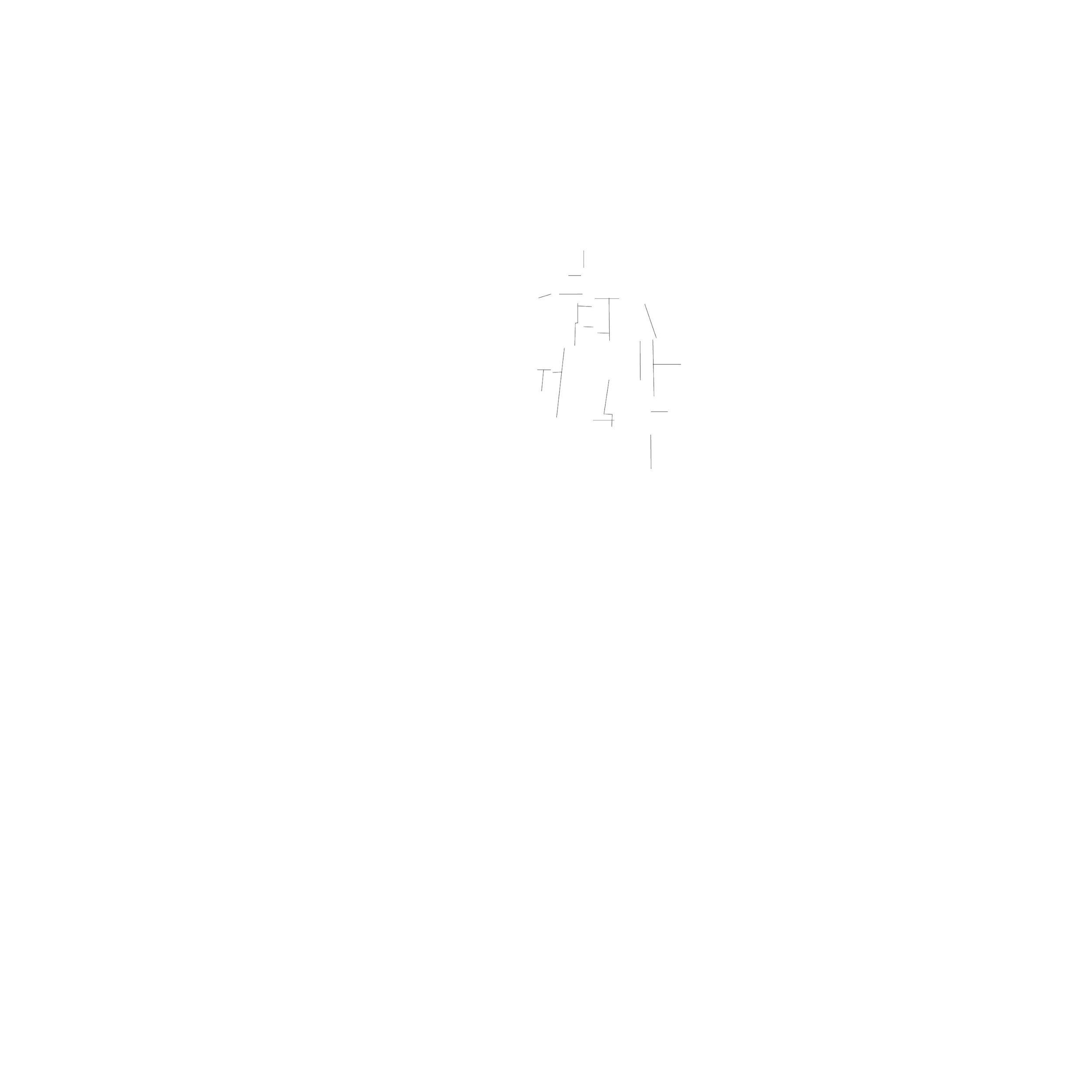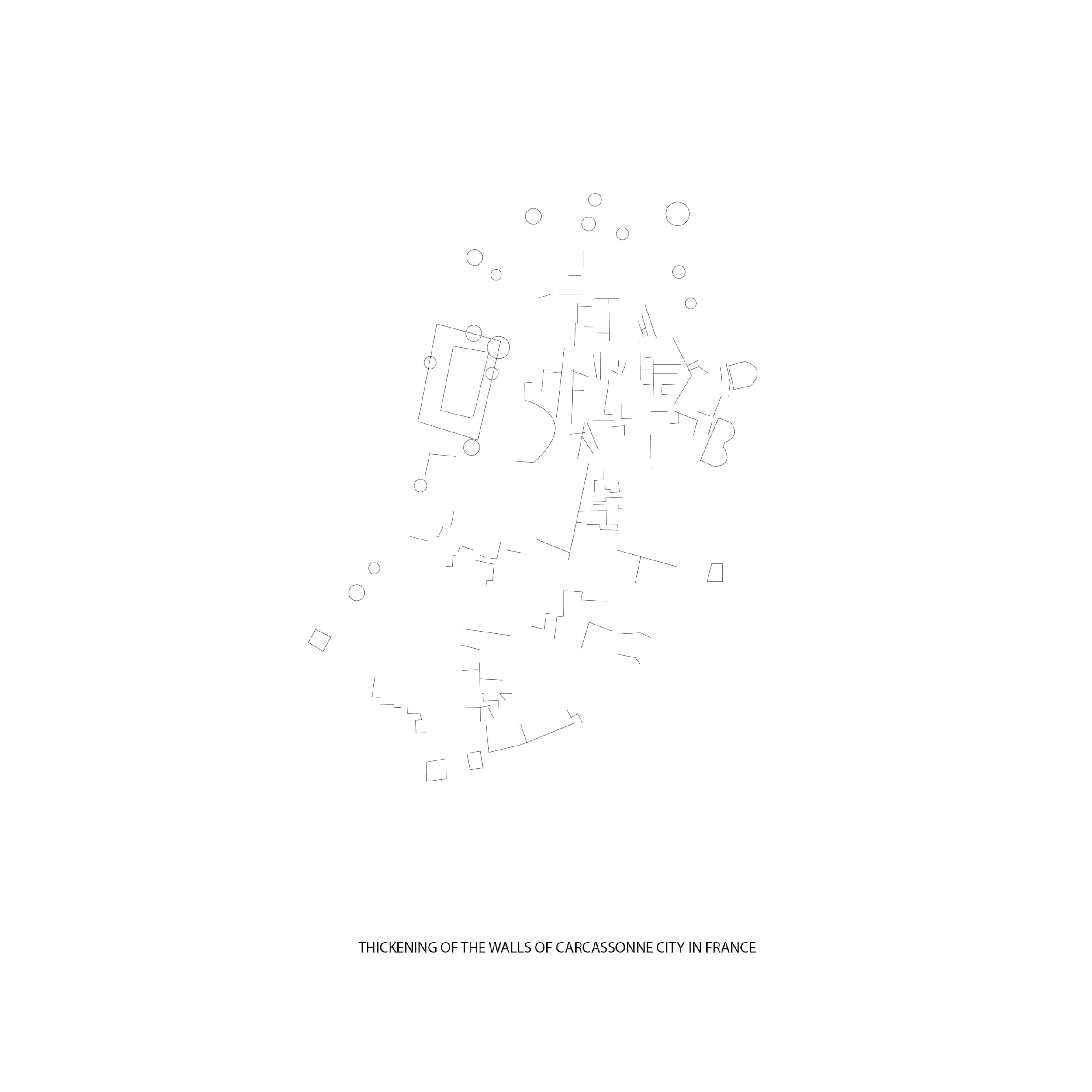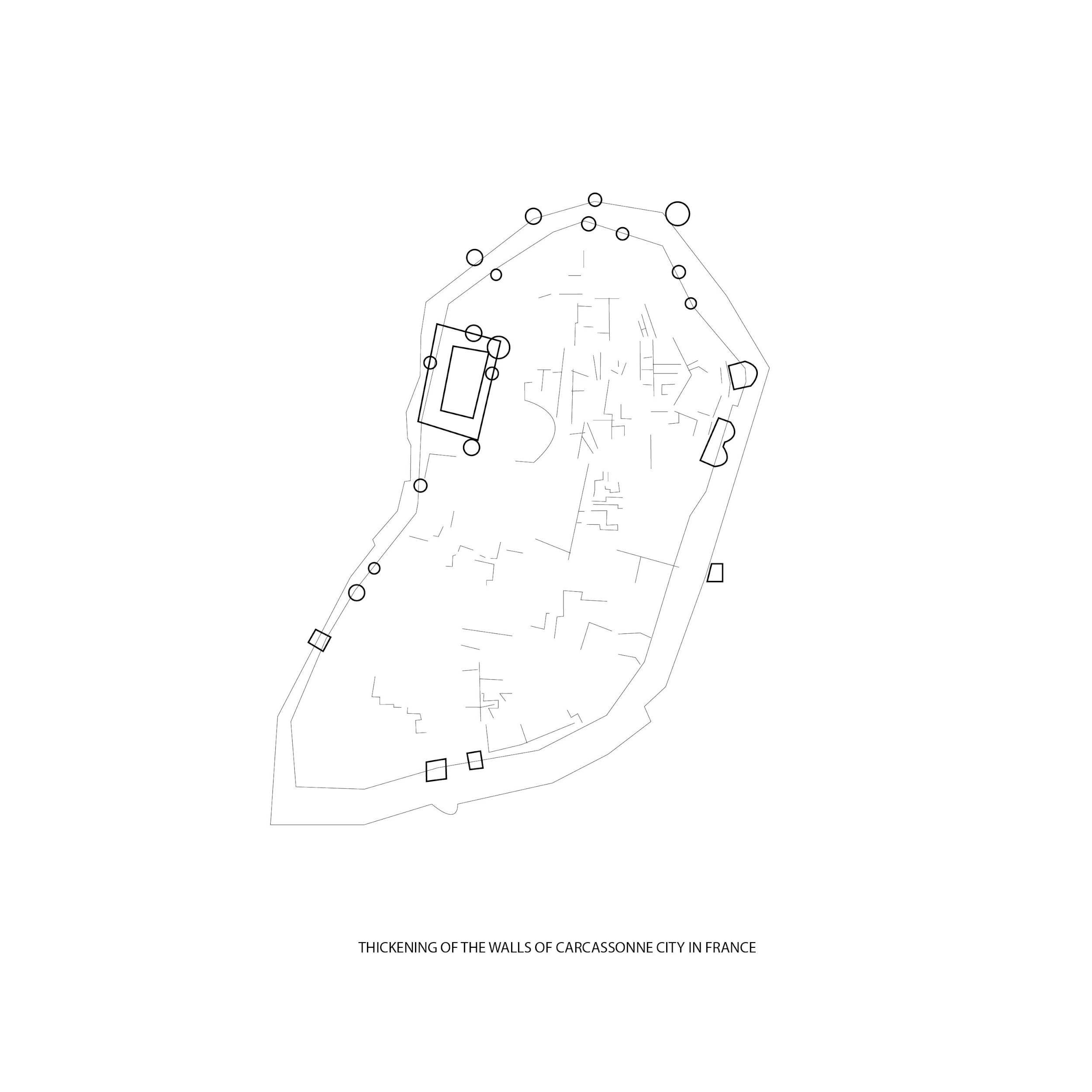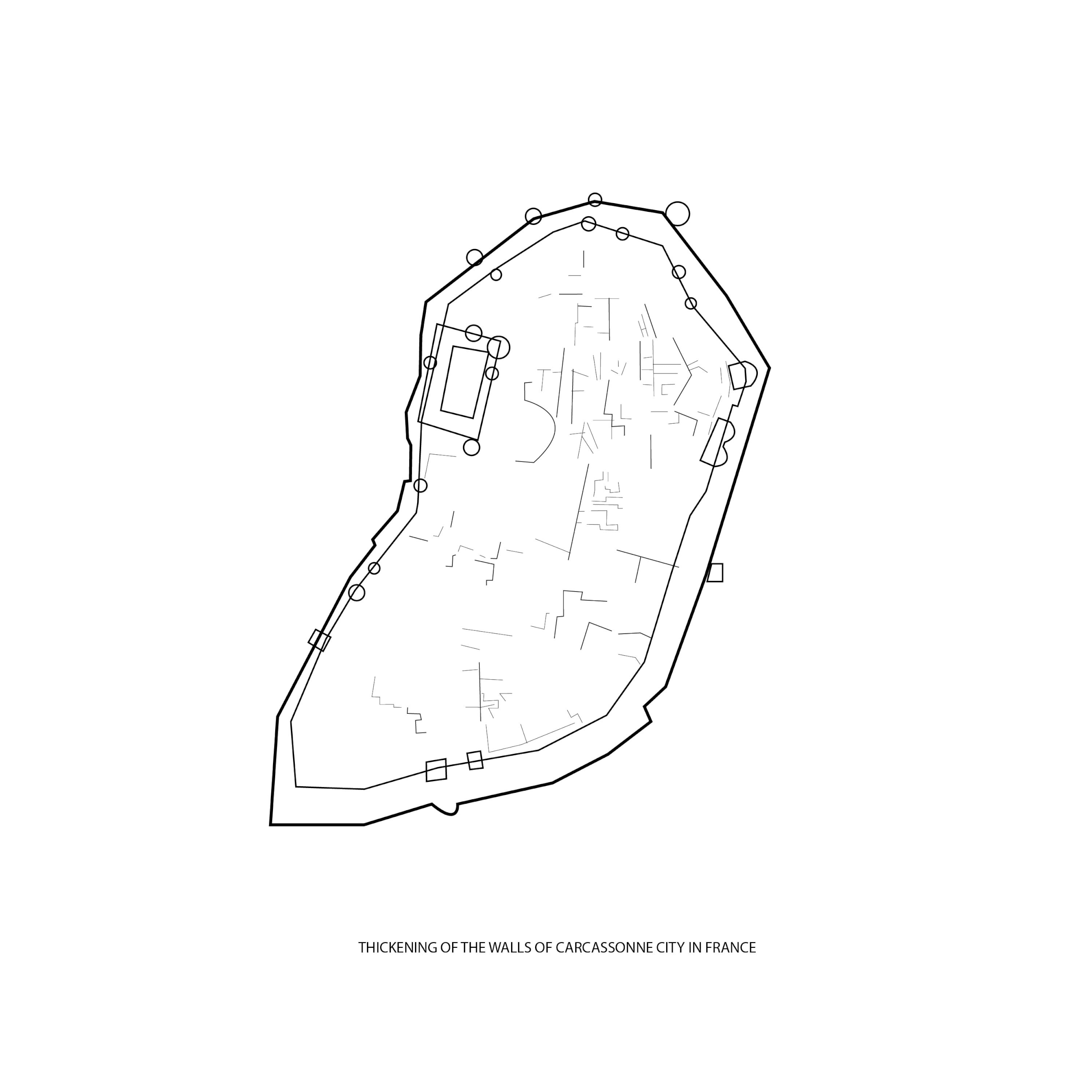Biomimicry = Sustainability
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Hyundai-RISD Collaborative
Research Process
Created by: Xinyi Liu
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________

____________________________________________
Three Fundamental types of systems in nature
Decentralized Systems _ Self-organized systems _ Adaptive systems
____________________________________________

____________________________________________
Examples:
____________________________________________
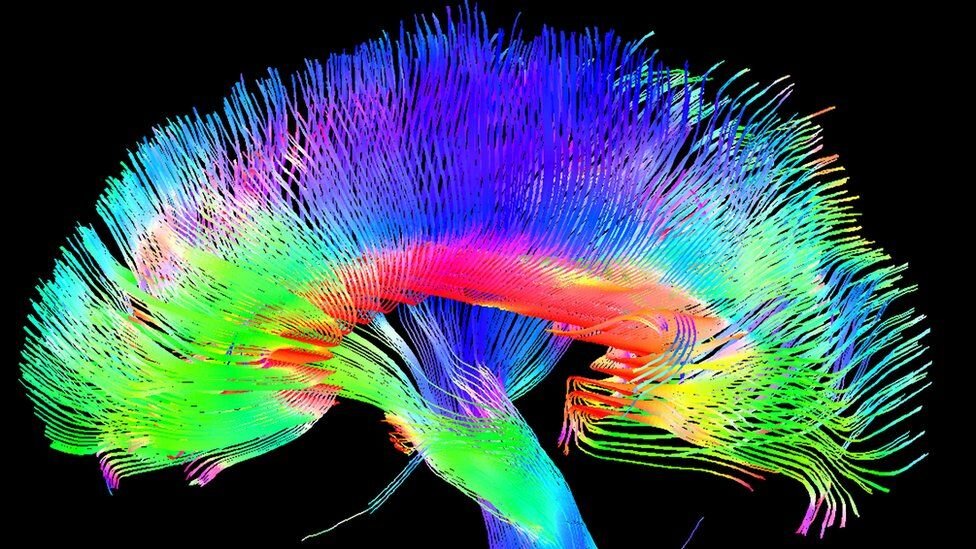
1. Brain’s Neural Circuits at a Microscopic Scale.
2. Ice Crystallization Process under a Microscope
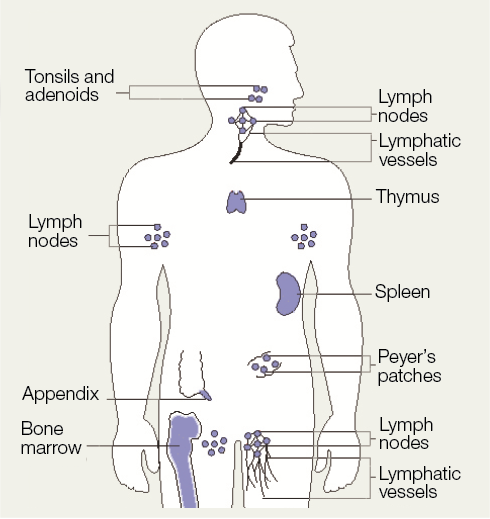
3. The adaptive immune response is provided by the lymphocytes, which precisely recognize unique antigens (Ag) through cell-surface receptors.
Receptors are obtained in billions of variations through cut and splicing of genes and subsequent negative selection: self-recognizing lymphocytes are eradicated.
Immunological memory after an Ag encounter permits a faster and heightened state of response on a subsequent exposure.
Lymphocytes develop in primary lymphoid tissue (bone marrow [BM], thymus) and circulate towards secondary lymphoid tissue (lymph nodes [LN], spleen, MALT).
____________________________________________
More Information on the Three Systems:
____________________________________________
different kinds of brain circuits
2. how crystallization is effected by temperature and chemical characteristics. This image shows different kinds of chemicals.
Consciousness:
_______________________________________
Theories and Mechanisms and Relationship to Urban Planning
Mar. 4, 2021
What is consciousness? Neuroscience Theory / Quantum Theory
How does sensory experience affect awareness / consciousness? E.g. How does sight influence decision-making
How does collective social consciousness/subconsciousness inspire the urban planning process?
____________________________________________

____________________________
Definition of Consciousness:
Overall, throughout the evolution of mankind, the human brain has been developed into three main parts: the instinctive survival brain, the emotional brain, and the logical brain. The awareness created by the brain enables us to be clear about our state of being and the surrounding environment.
____________________________
____________________________
Three Main Parts of the Brain:
Neocortex (complex reasoning),
Limbic System (Emotional activities)
Reptilian Brain, Amygdala (basic function of the body/survival brain)
____________________________
____________________________
The origin of consciousness
The cerebral cortex is the largest site of neural integration in the central nervous system. It plays a key role in attention, perception, awareness, thought, memory, language, and consciousness.
(In the Neuroscience Theory of consciousness)
____________________________



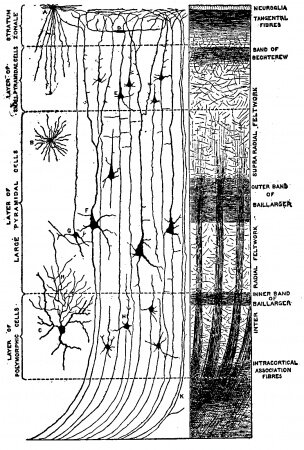

____________________________
Detailed Parts in the Brain
The core of emotional brain activity seems to be the limbic forebrain: the thalamus, the hypothalamus, the reticular formation, and the amygdala, all of which are subcortical (below the cerebral cortex). The hypothalamus has important links to pleasure and misery, while the reticular formation may have an important link to depression.
____________________________
The philosophical structure of mind
(study based on Hannel’s “Master Key System”)
Subconsciousness (passive information collection)
Consciousness (initiative information)
Reality
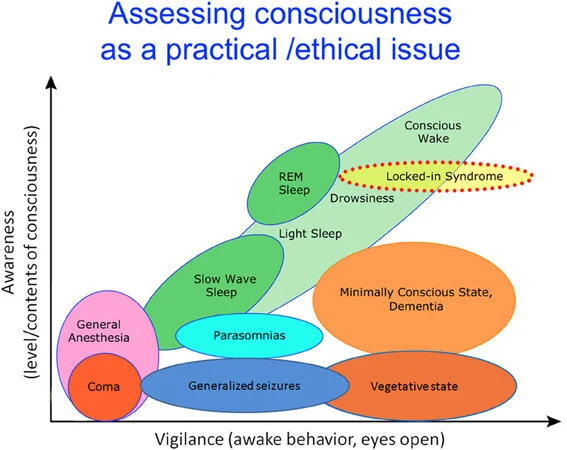
Consciousness to different cognition states
This diagram shows how different levels of consciousness are related to corresponding mental and behavior status.
the relationship between the conscious mind and the subconscious mind.
_________________________________________
Three Types of Systems
that Demonstrate “Energy”
how sight is formed in the brain nutrition transferring process in a leaf electromagnetic induction between neurons
_________________________________________
How sight is created from the eyes to the brain?
Vision begins with light passing through the cornea and the lens, which combine to produce a clear image of the visual world on a sheet of photoreceptors called the retina. As in a camera, the image on the retina is reversed: Objects above the center project to the lower part and vice versa. The information from the retina — in the form of electrical signals — is sent via the optic nerve to other parts of the brain, which ultimately process the image and allow us to see.
Retina has many visual cells serve as image receptors, which transform the information from the sight to the brain in next step.
In the brain, there are several areas that response to the visual signals from the retina(the visual cells in the eyes). This information is sent to many areas in the brain which translate different content to our consciousness.
The three main types of information are ”what, where, and how.”
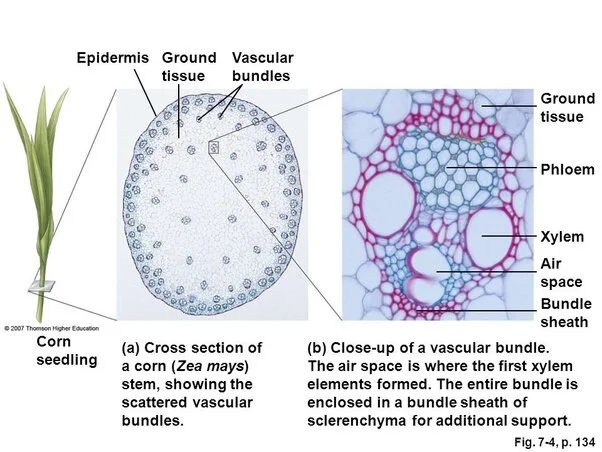
2. nutrition transferring process in a leaf
cells in a leaf
A larger scale of leaf cells :
their location and organization





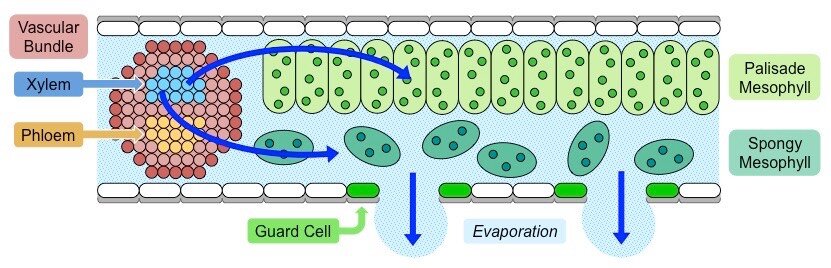
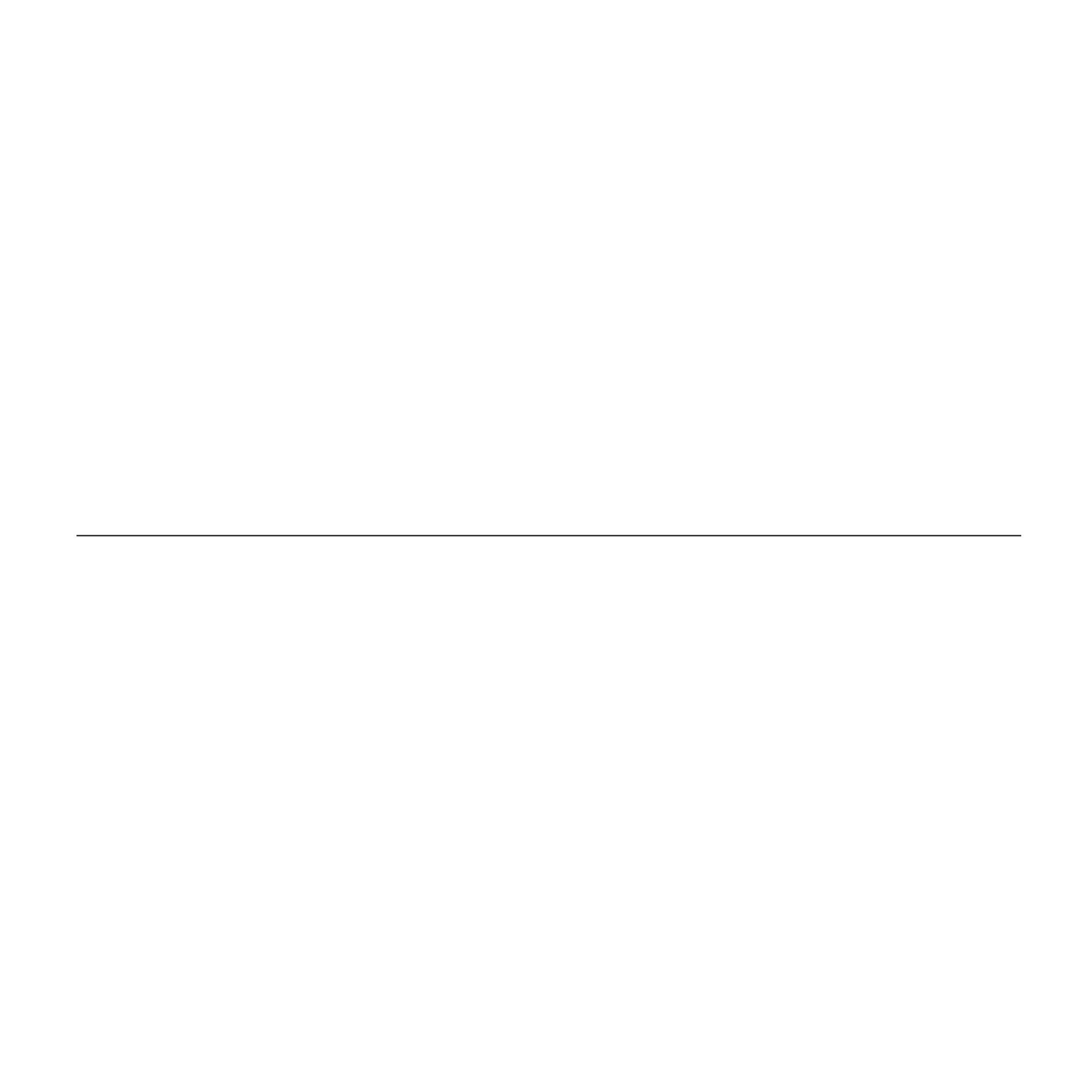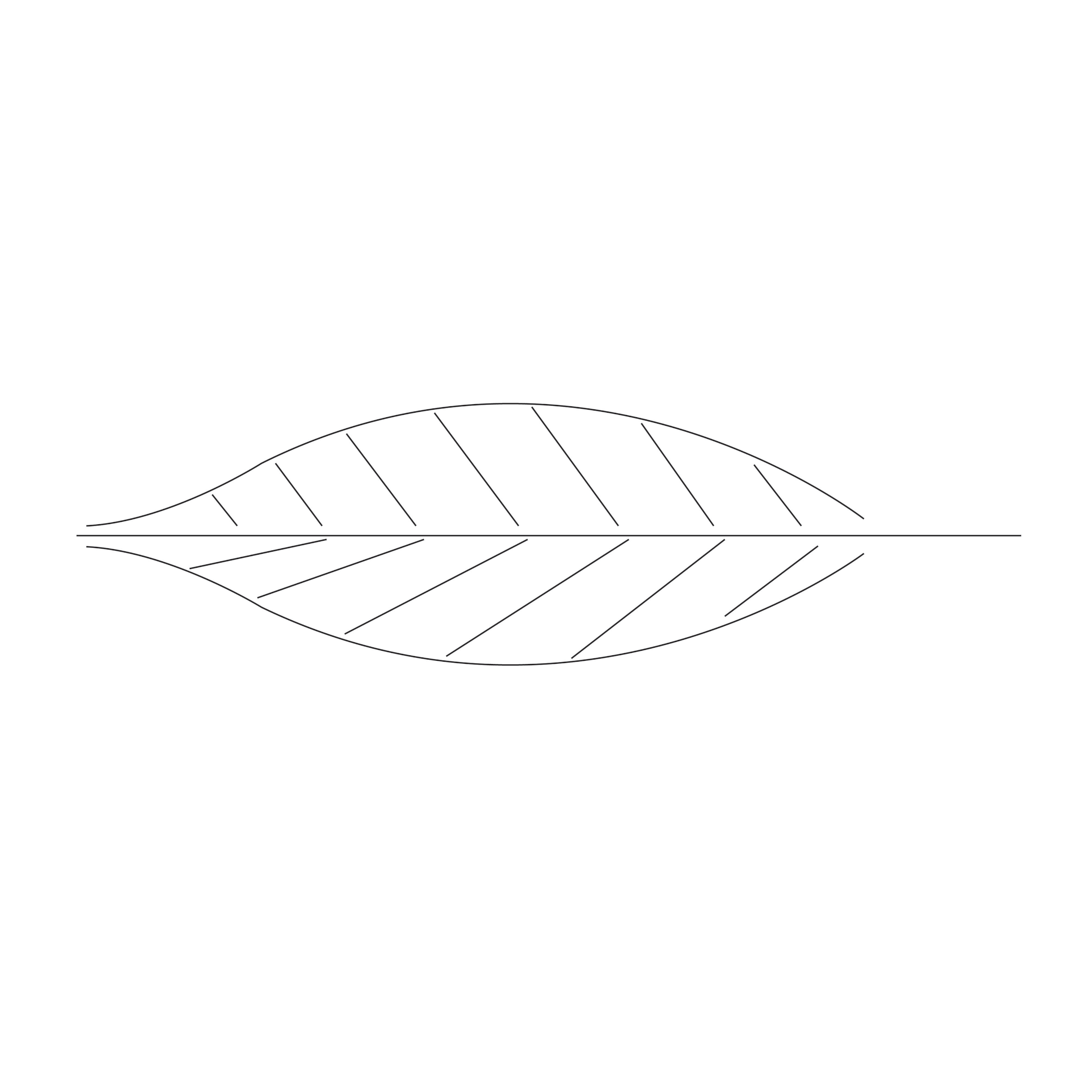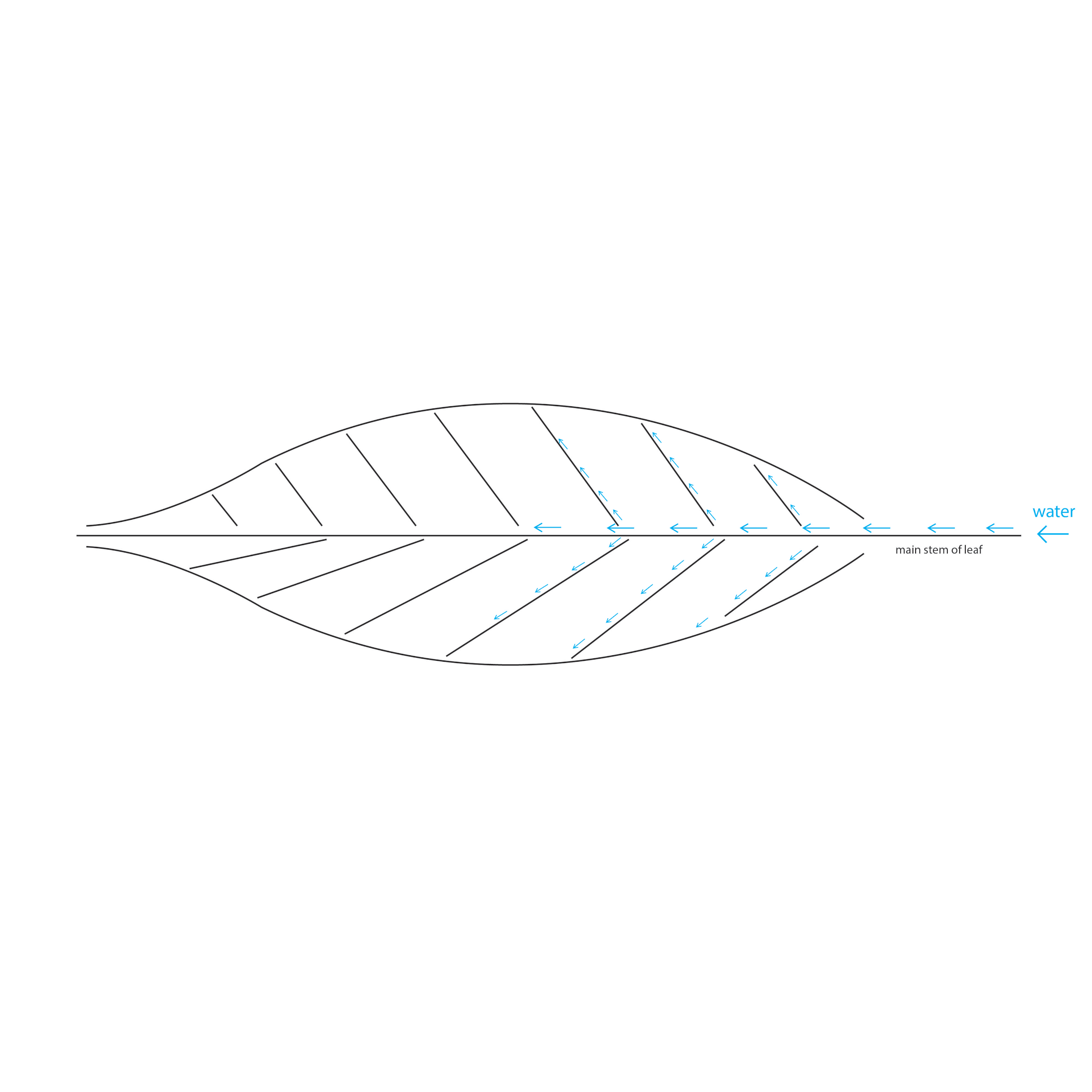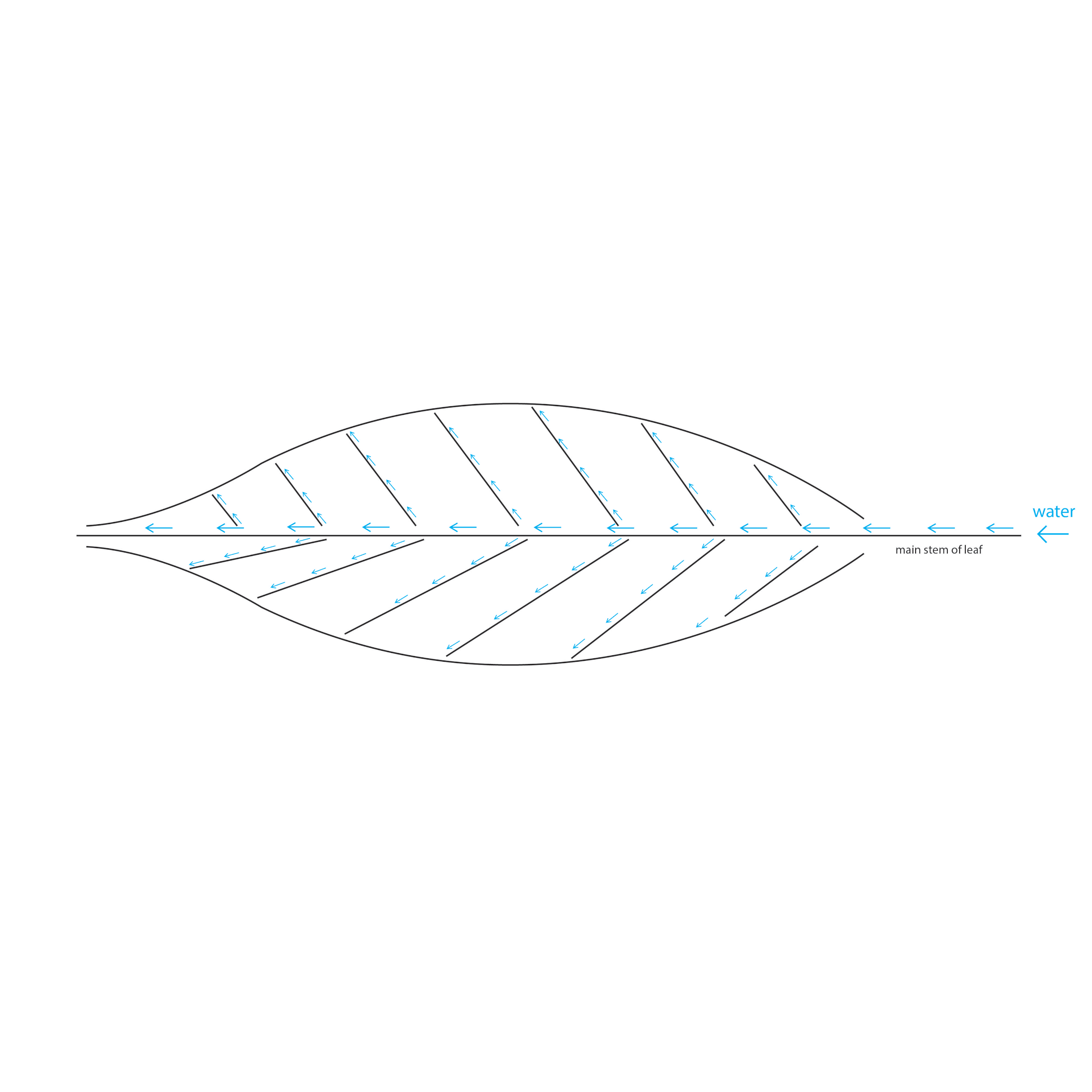
Energy inside of the leaf: how does water pass through the gap and react to the leaf cell of a corn leaf?




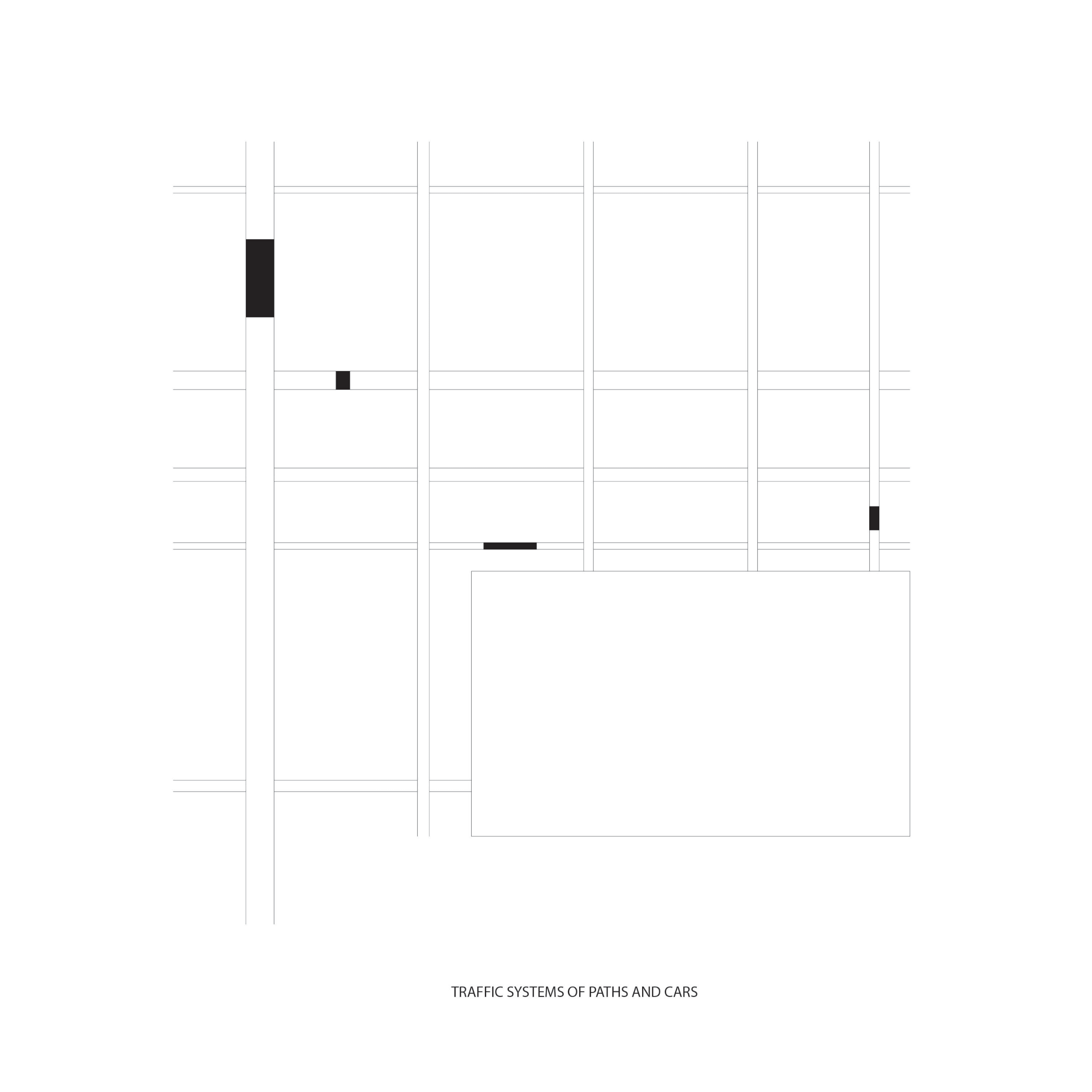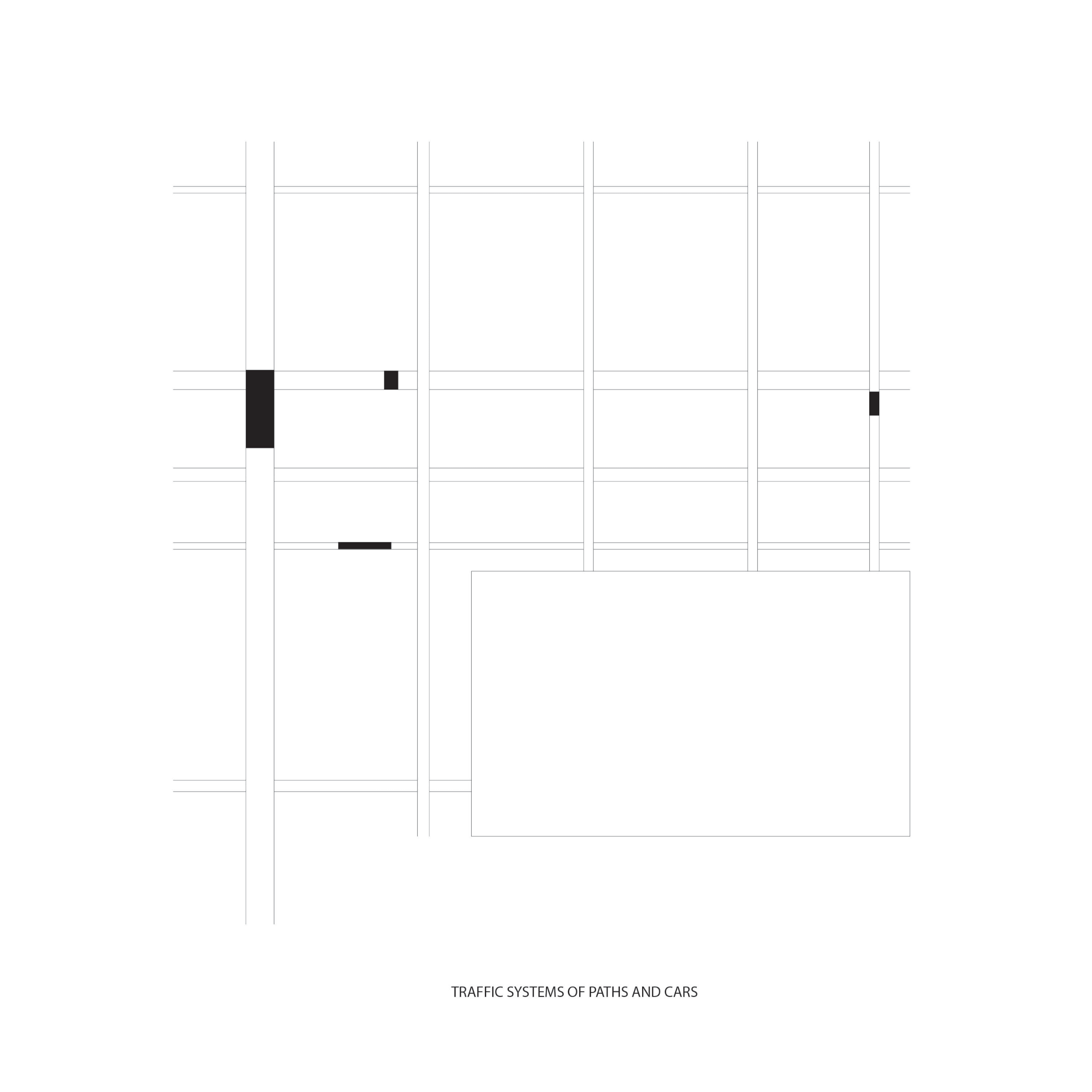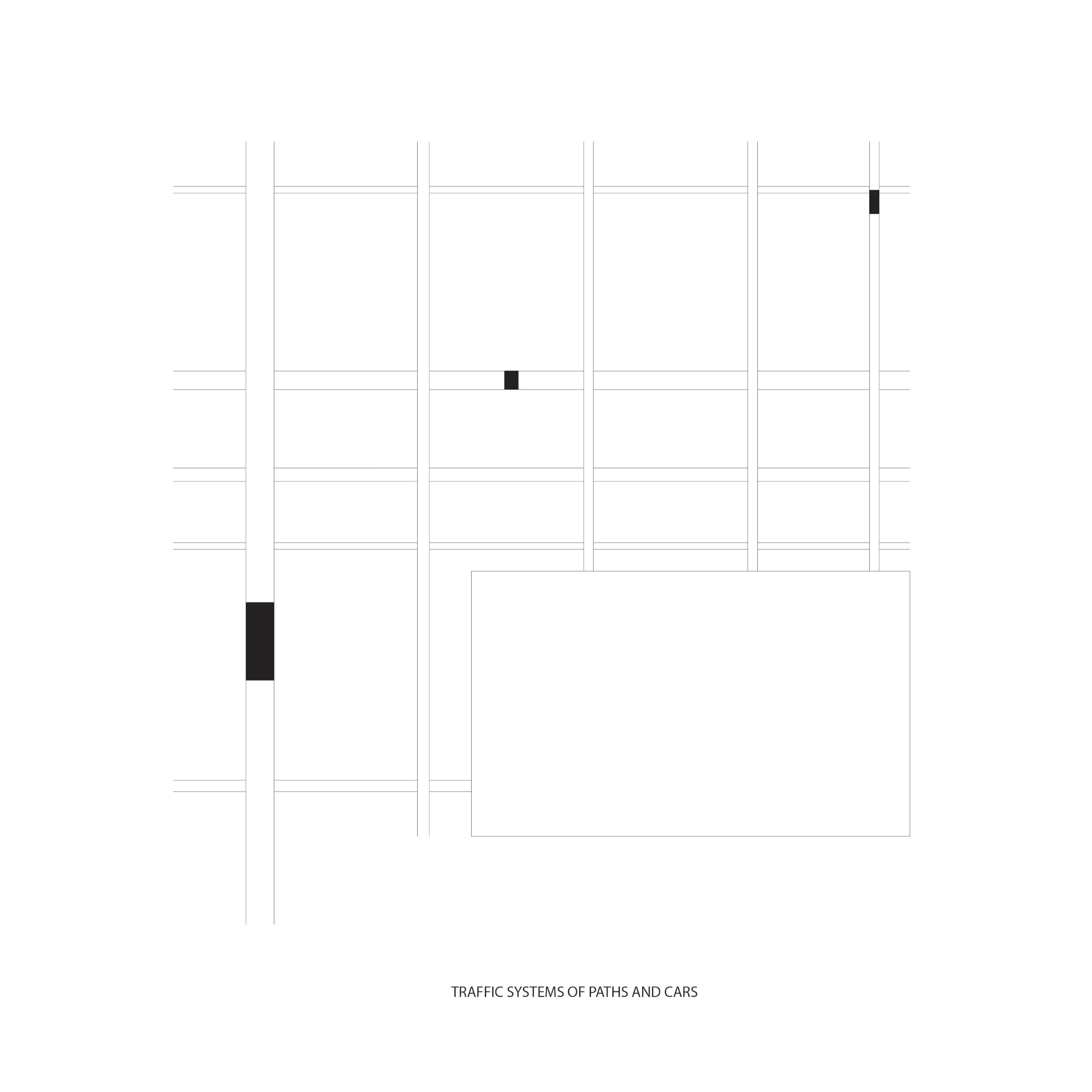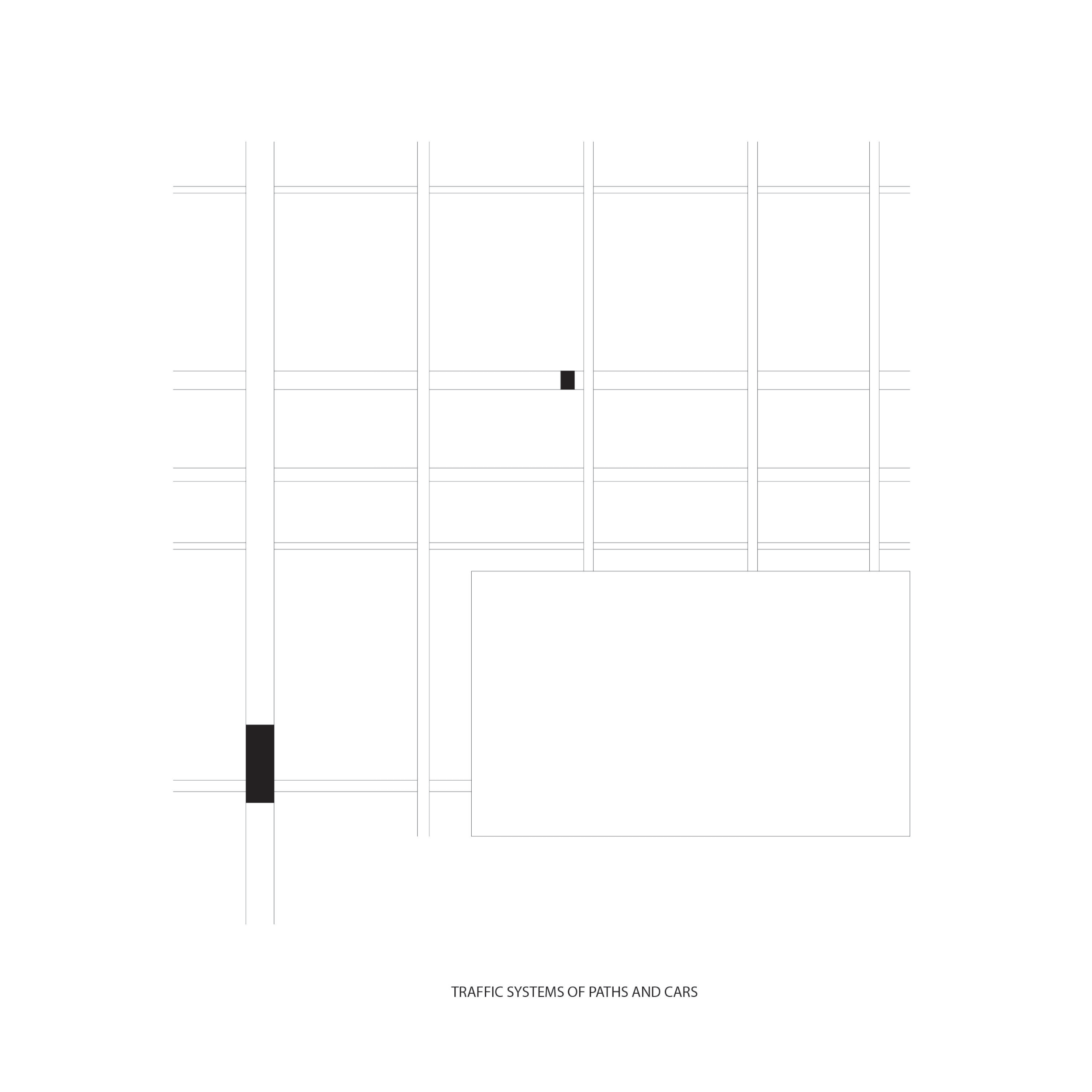
Traffic systems of paths and cars
vs.
water supply paths among leaf cells
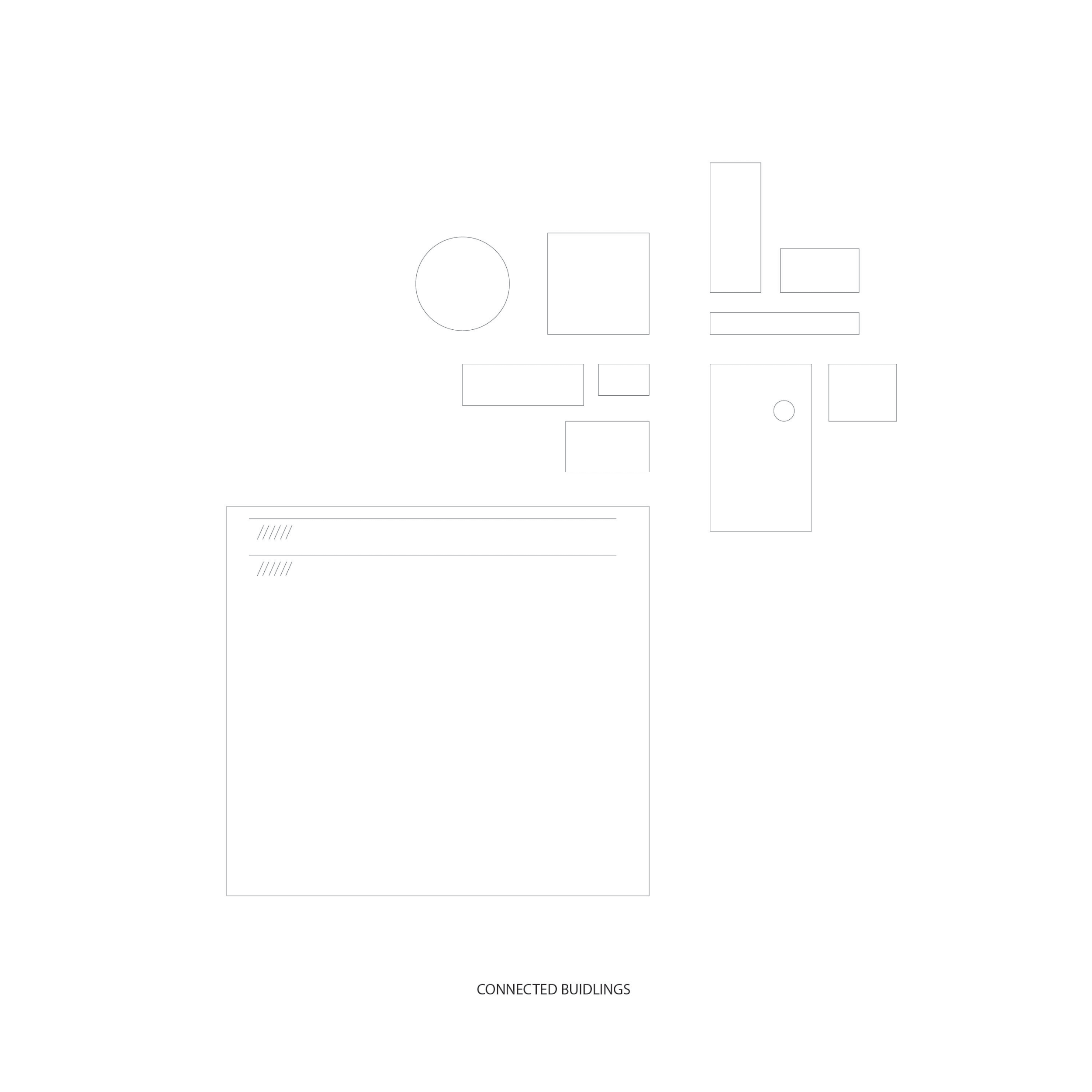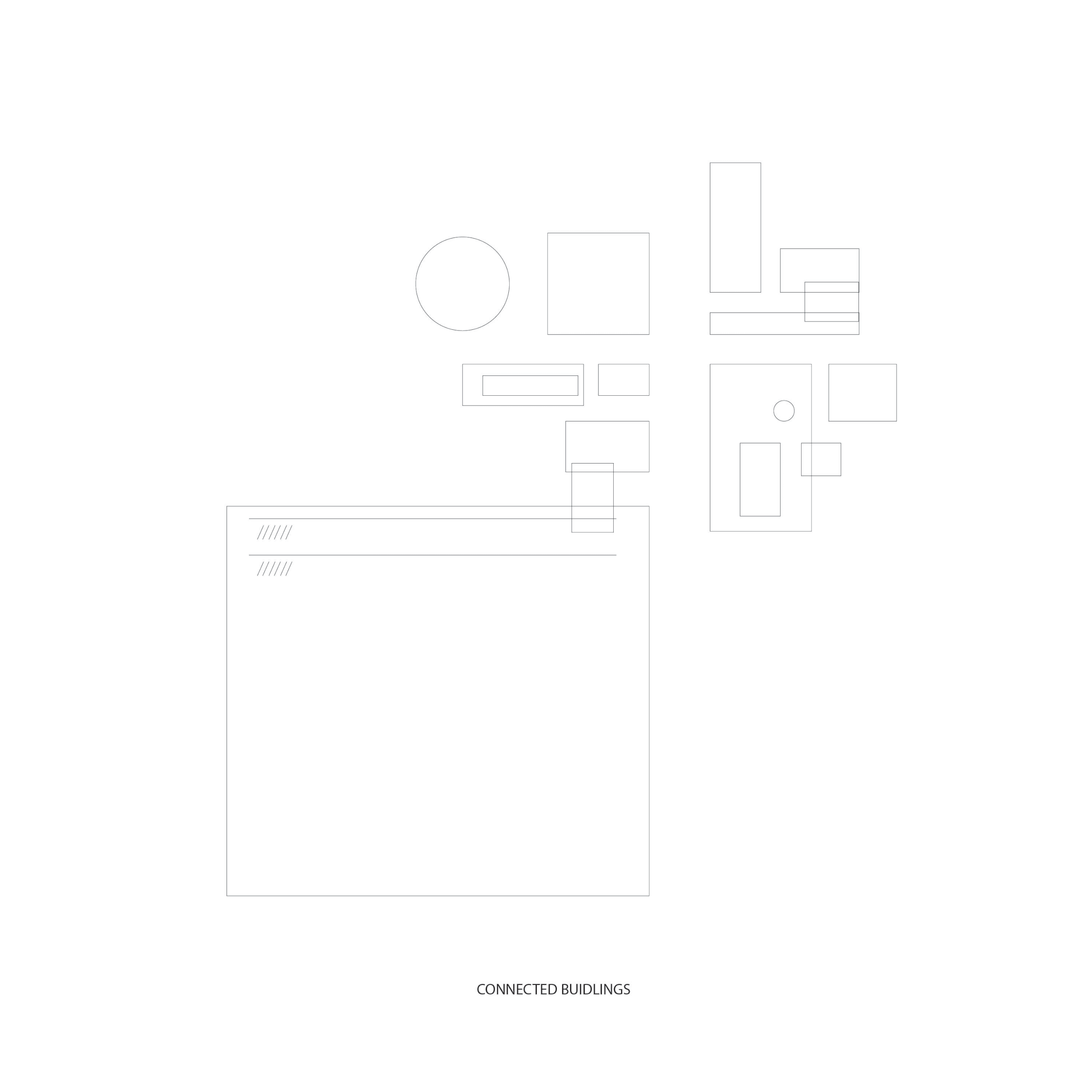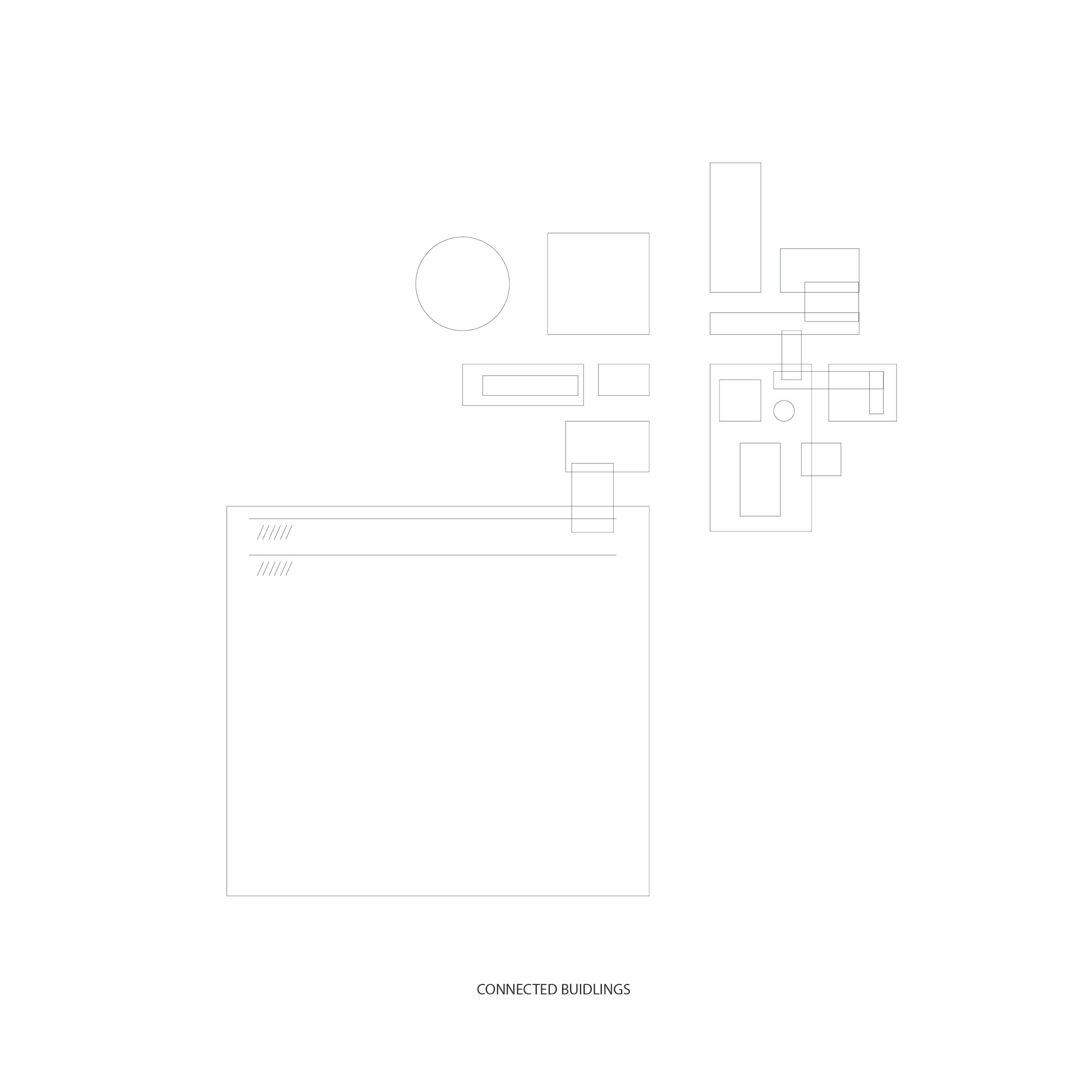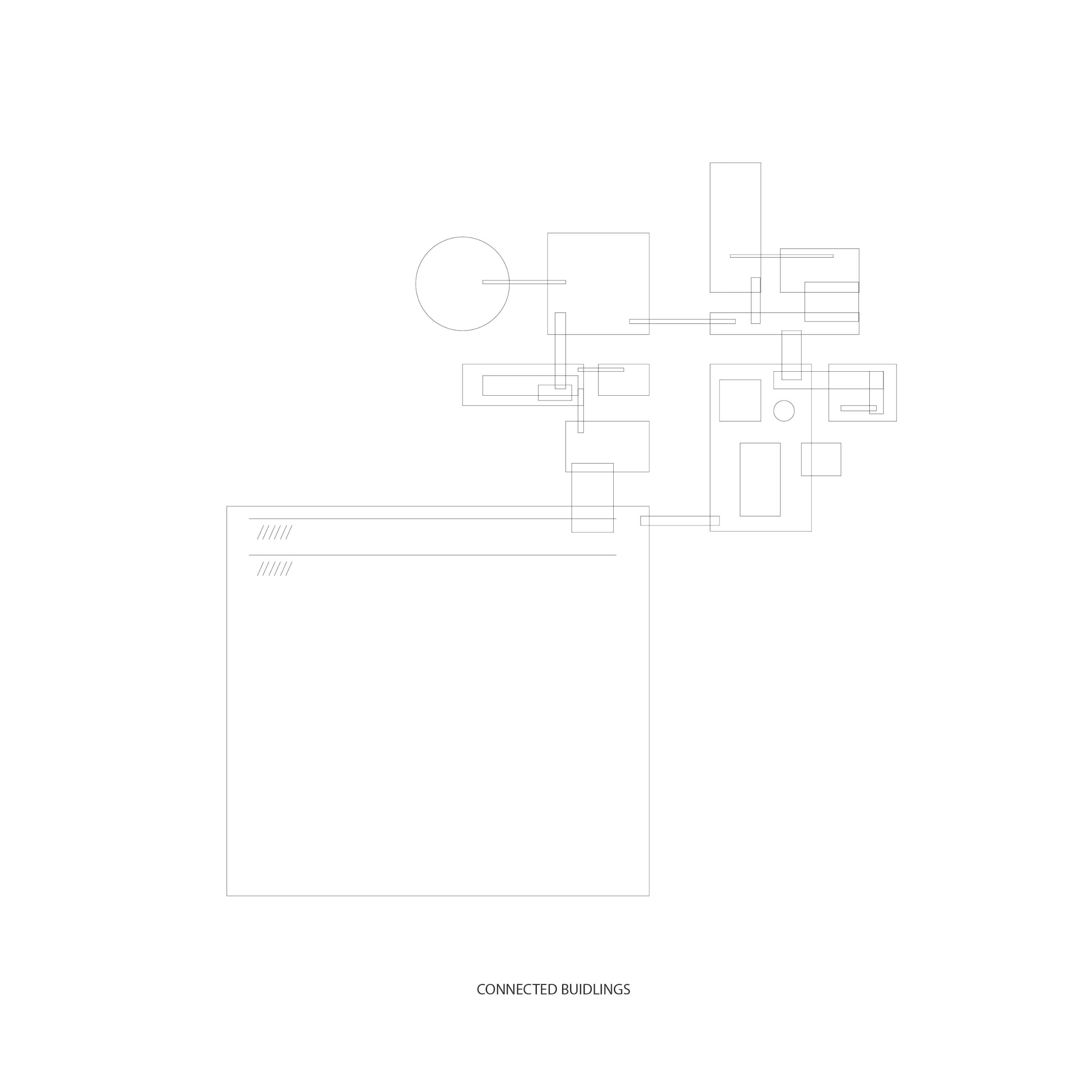
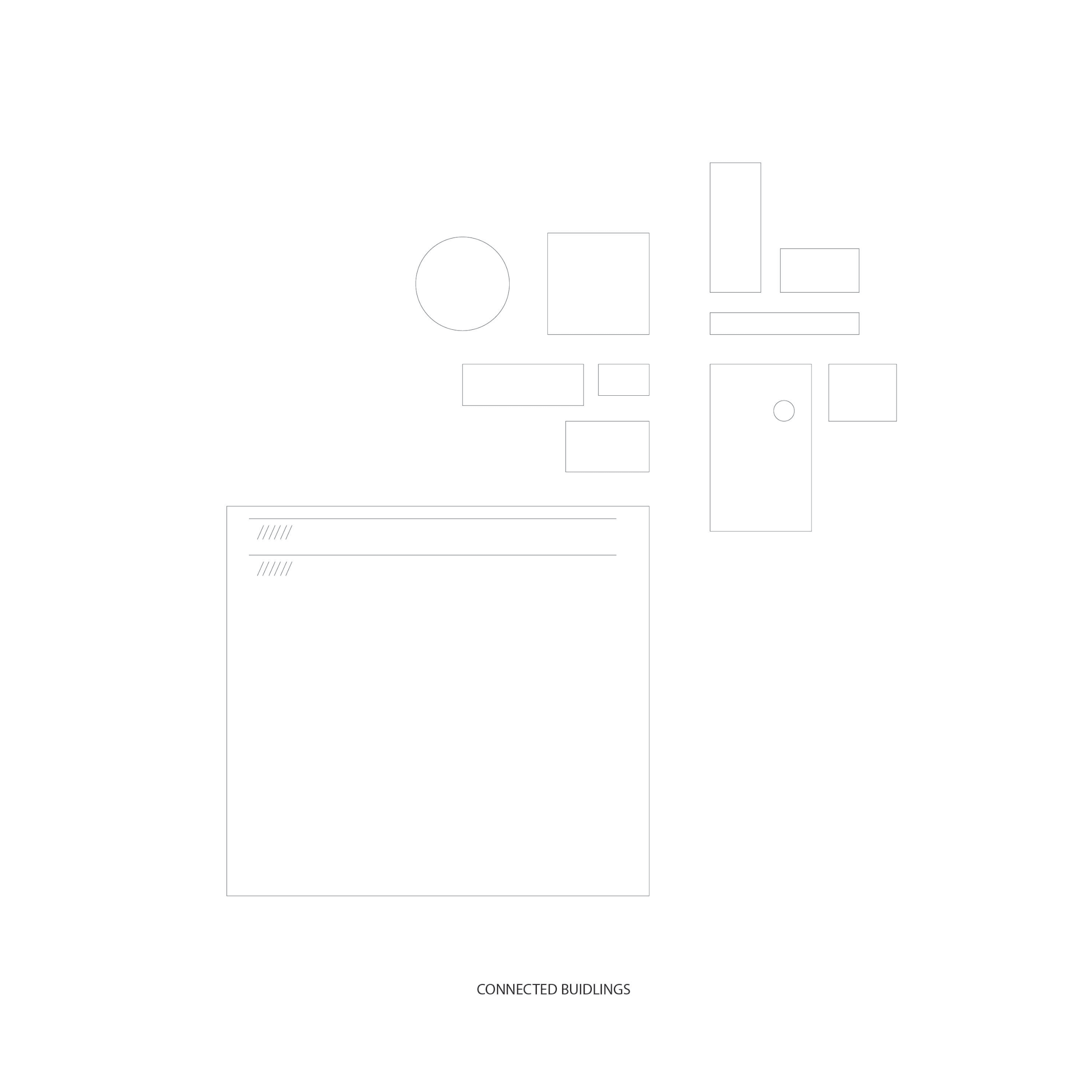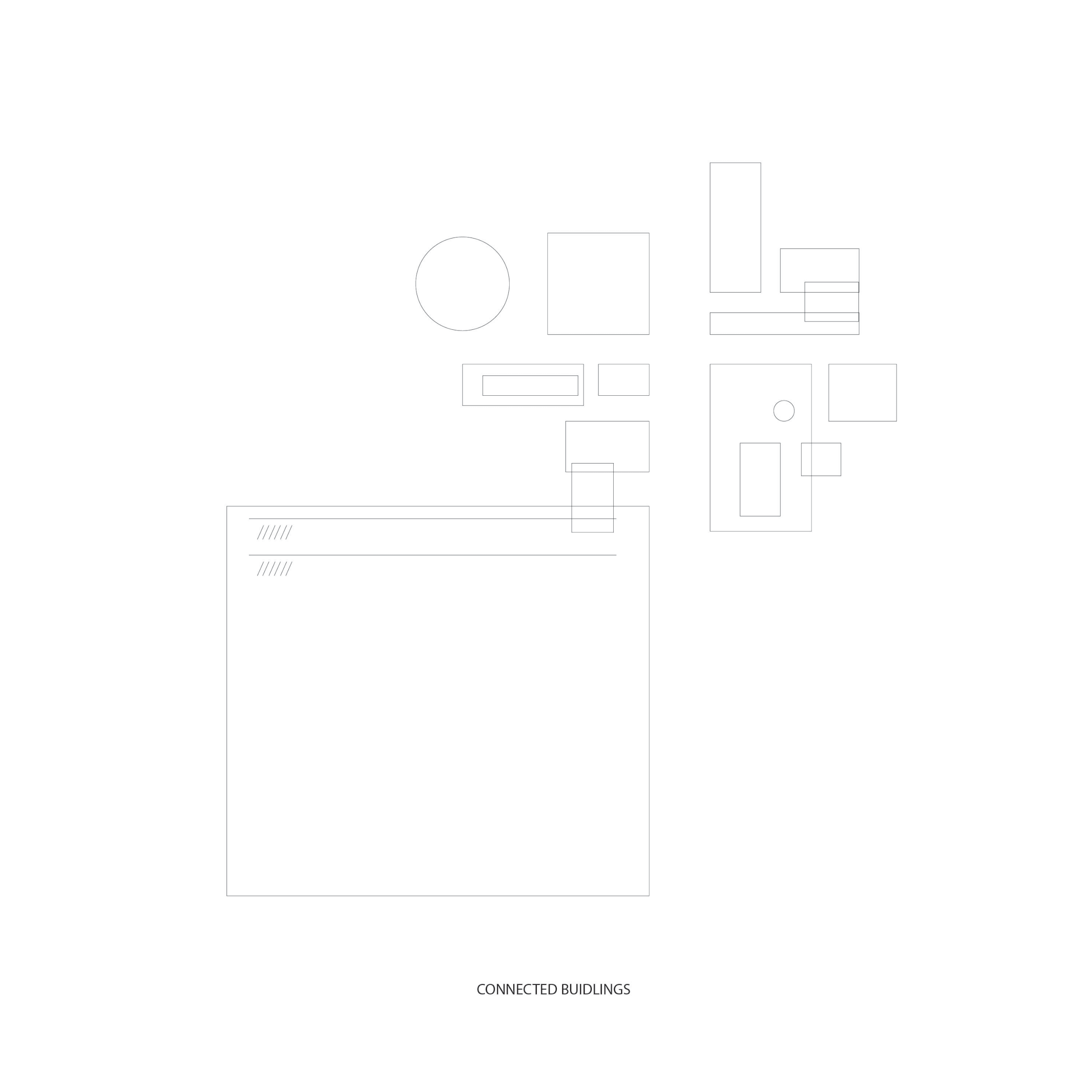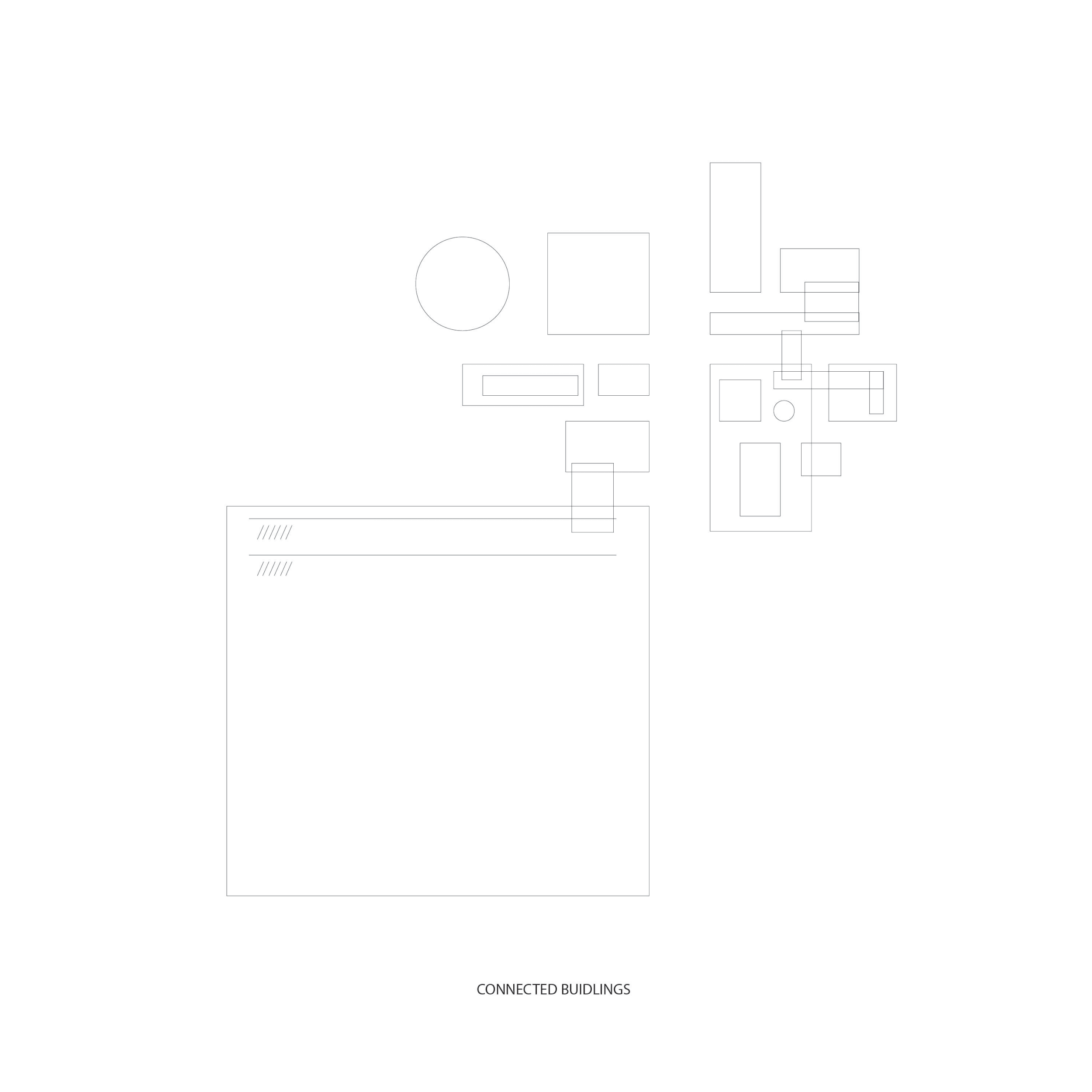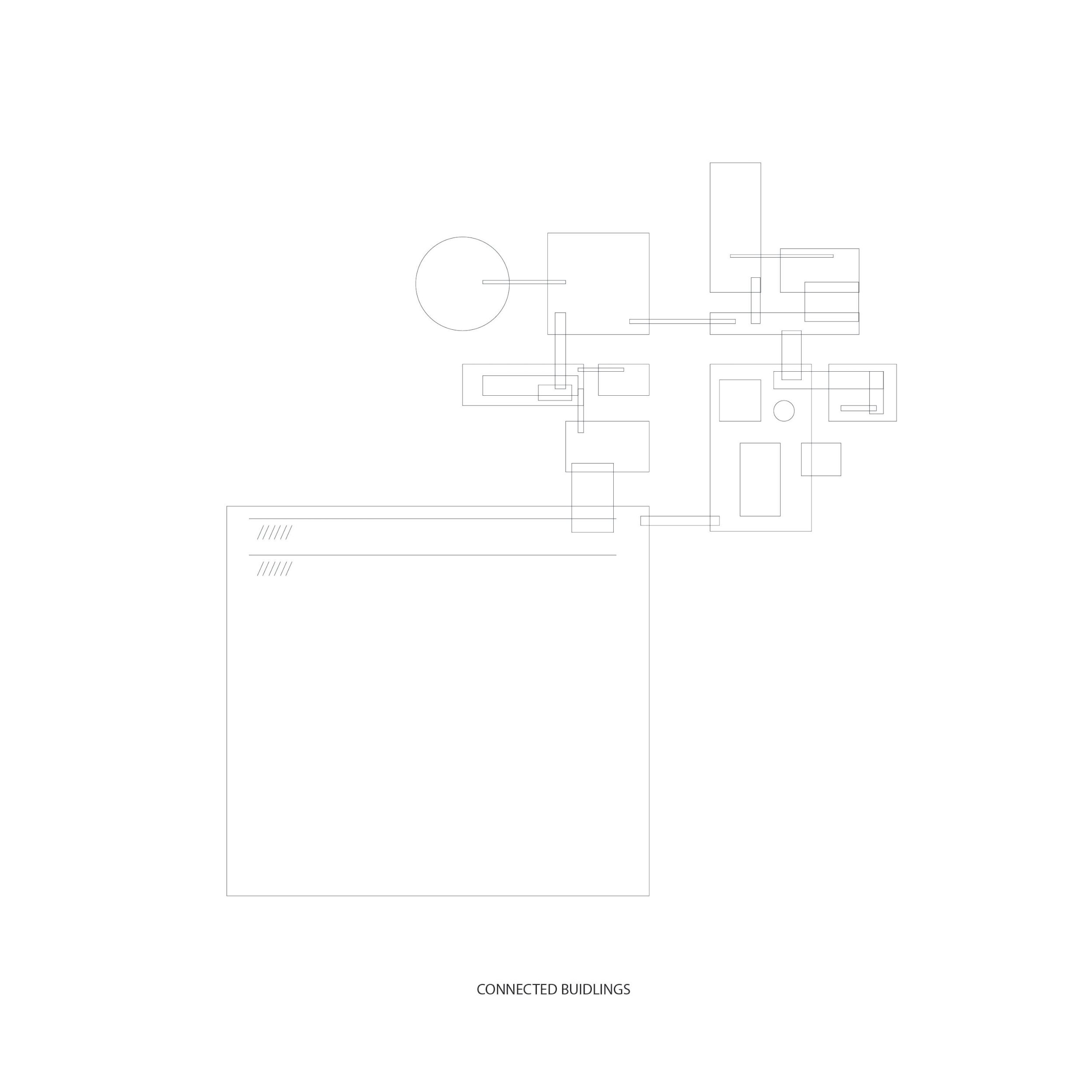
Connected buildings
vs.
Intercellular physical and chemical reactions within a leaf
Expansion of the Medieval city of Carcassonne in France
vs.
How does a leaf form? This diagram shows an analogy of a leaf cell using the expansion model of Carcassonne: with substances, enzyme receiver, and membrane as the cell structures.
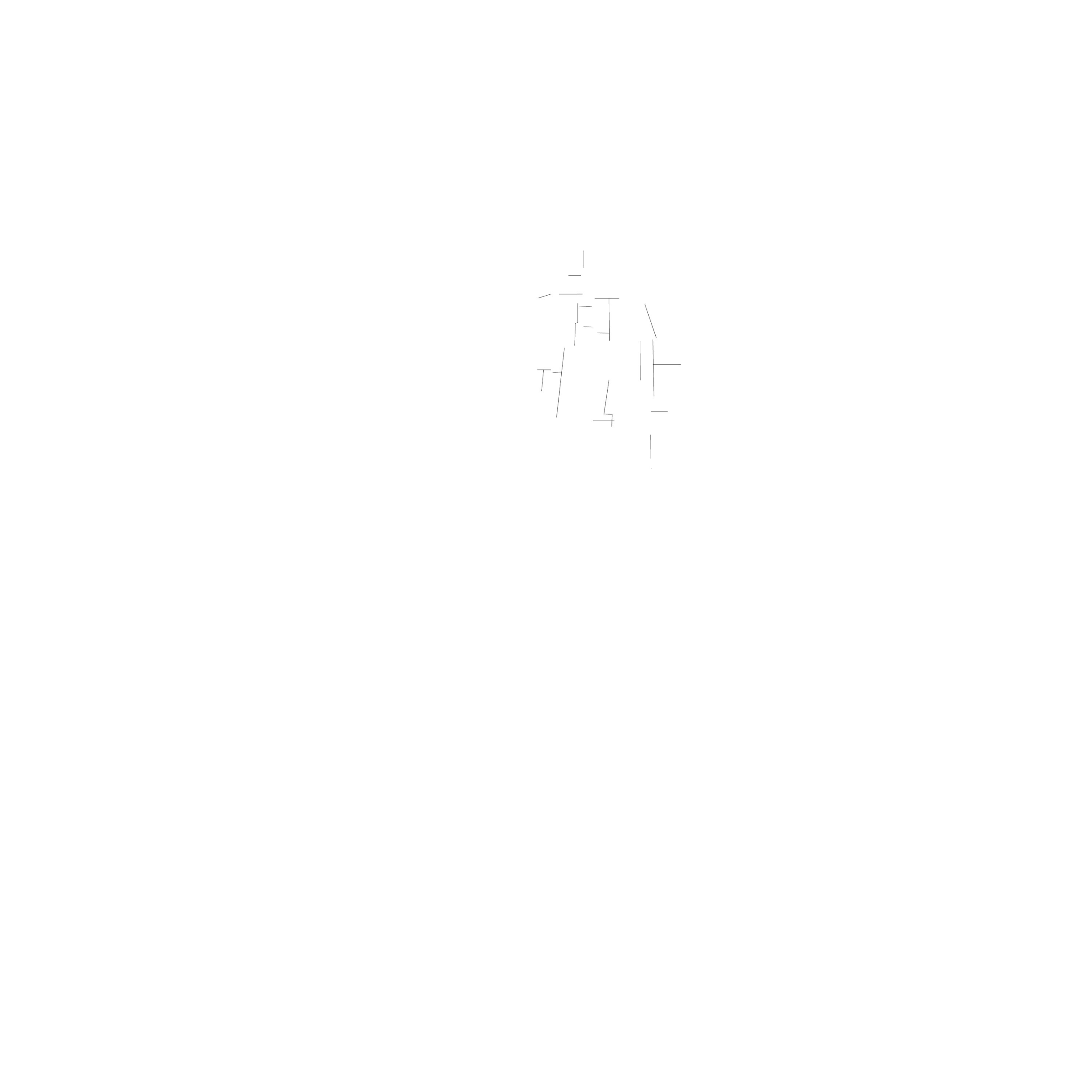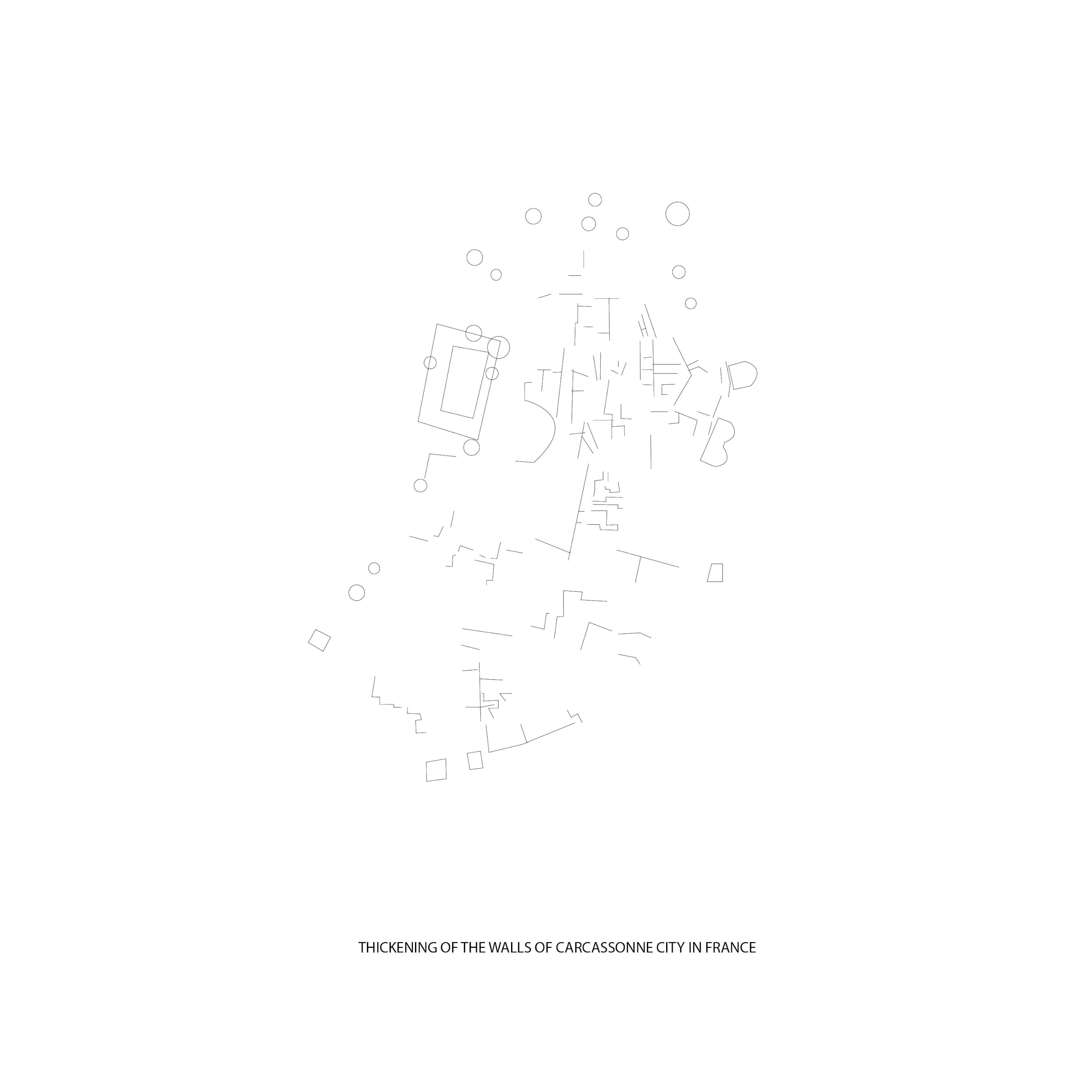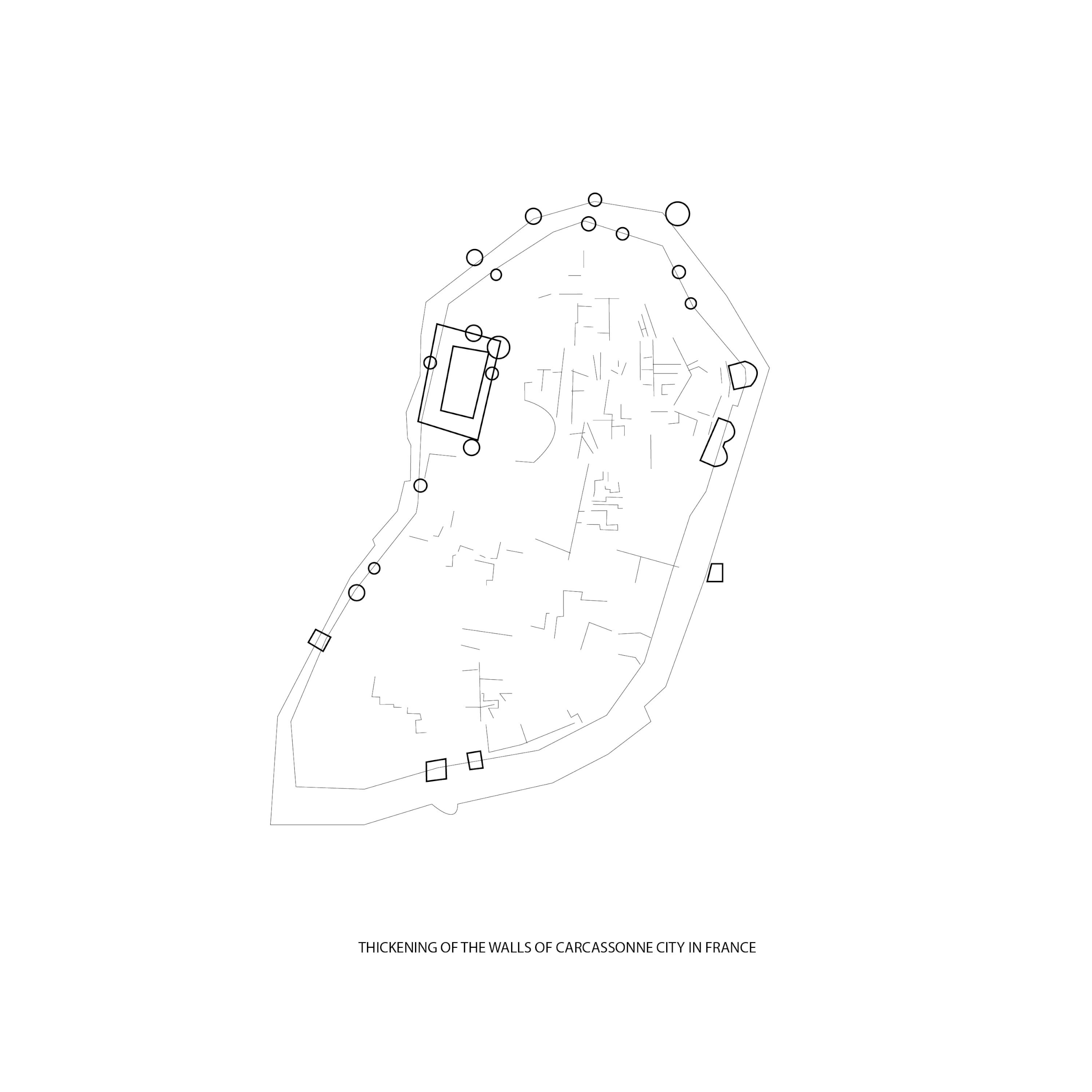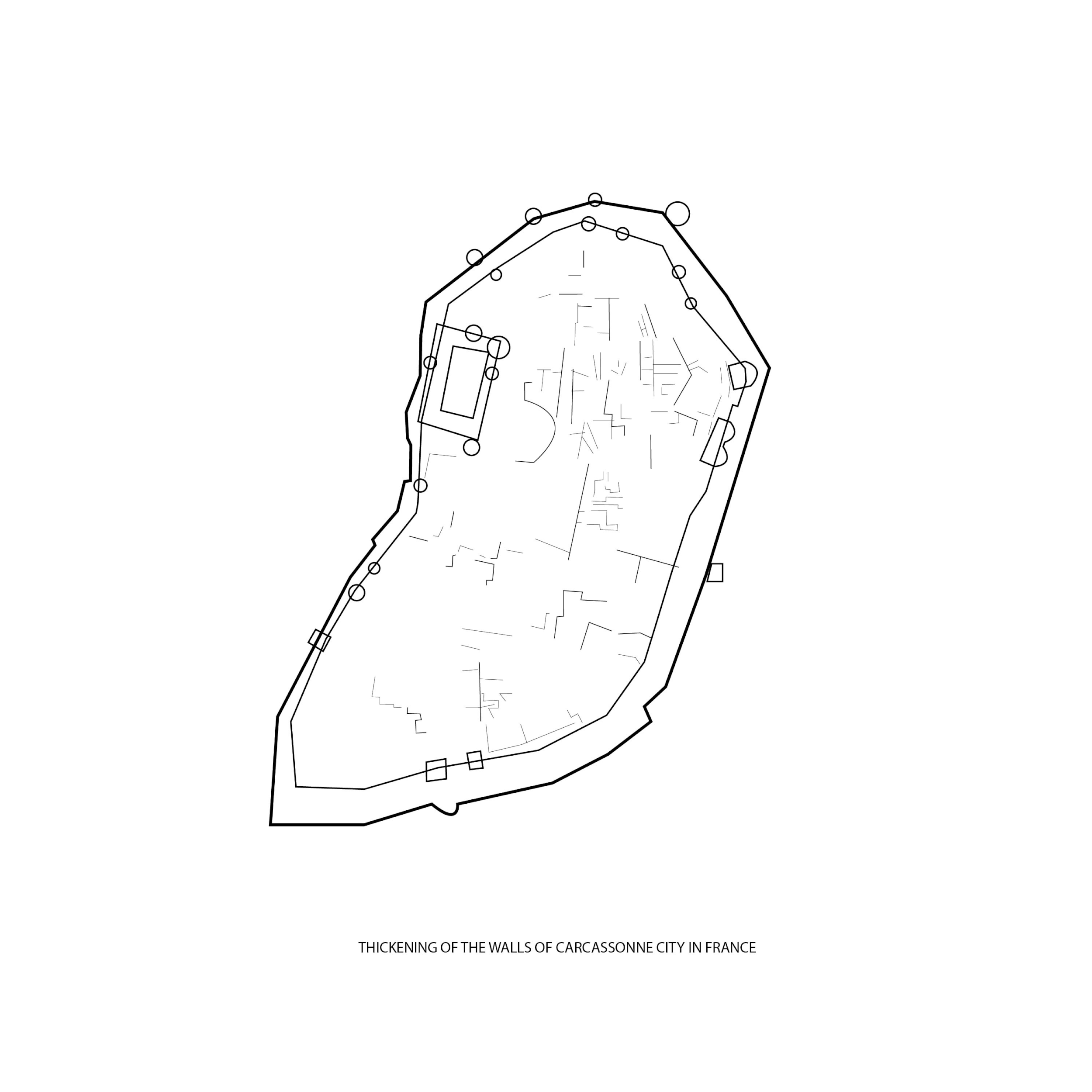
Urban System Research
_____________________
Urban system I’m interested in: future configuration of living space under the background of global population growth in the urban area.
Scale: a large modern city, especially in the developing country in Eastern Asia
Layers of connectivity: 1. people to infrastructure. 2. infrastructure to infrastructure. 3. people to people. 4. individual space
Primary issue: limited living space for each person, reducing resources available for individual activity, increasing land and housing price. Competitive job market. Traffic jams.
Type of interaction involved: competition among people for sustaining their quality for making a living.
Actors and stakeholders involved in the interaction: government, urban planners, architects, capitalist, individual people who need better living space in the future, especially homeless people.
Natural resources involved: public greenery, such as public gardens on ground level, national forests, vertical gardens, etc.
Urban issues related to these natural resources: limited space for natural resources because of expanding constructions for growing population in the urban area.
Critical factor for maintaining the sustainability of the urban system: reasonable governmental control and awareness of effective environmental justice.
Population, Urban Growth Pattern and Topology, Issues, and possible design solutions for the future
Population Expansion in the Urban Area
Urban Growth Patterns and Layouts
Urban Green Area Solutions and Layouts
Future transportation system
The compact city or city of short distances is an urban planning and urban design concept, which promotes relatively high residential density with mixed land uses. It is based on an efficient public transport system and has an urban layout which – according to its advocates – encourages walking and cycling, low energy consumption and reduced pollution. A large resident population provides opportunities for social interaction as well as a feeling of safety in numbers and "eyes on the street".[1] It is also arguably a more sustainable urban settlement type than urban sprawl because it is less dependent on the car, requiring less (and cheaper per capita) infrastructure provision (Williams 2000, cited in Dempsey 2010).[2]
My Interpretation for the Possible Solutions for Future Urban Development